| WV | DHHR | BPH | OEHP | HSC | PUBLICATIONS |
 "1999 Vital" Executive SummaryTables Population
Other Information MethodologyDefinitions Rates & Ratios ICD10 Groupings Credits Statistics and Trivia - You must use the "BACK" button to return to this page. Other on-line HSC publications can be found at: PUBLICATIONS The Health
Statistics Center is located at:
|
West Virginia Vital Statistics - 1999
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Population | Live Births | Deaths | YPLL | Infant Deaths | Neonatal/postneonatal deaths | Fetal Deaths | Marriages | Divorces and Annulments | Summary |
Population
For the third year in a row, more state residents died than were born. In 1999, 262 West Virginians were lost to the total population as a result of natural decrease, the excess of deaths over births. The rate of natural decrease was 0.14 persons per 1,000 population. Population estimates for 1999 show a total decrease in the state's population (approximately 0.2%) since 1998, from 1,811,000 to 1,807,000. This decrease is the result of the natural decrease and an excess of outmigration over inmigration.
Top of Page
Live Births
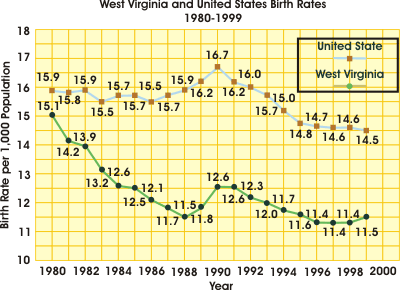
West Virginia resident live births increased by 2, from 20,729 in 1998
to 20,731 in 1999. The 1999 birth rate of 11.5 per 1,000 population was
slightly higher than the 1998 rate (11.4). The U.S. 1999 provisional birth
rate was 14.5 live births per 1,000 population, slightly lower from 1998
(14.6). As the graph below shows, West Virginia's birth rate first fell
below the national rate in 1980. It has continued its overall decline,
interrupted by slight upturns between 1989 through 1991 and 1999.
 The 1999 U.S. fertility rate of 65.8 live births per 1,000 women aged
15-44 was 0.3% higher than the 1998 rate (65.6). West Virginia's fertility
rate increased from 53.7 in 1998 to 56.3 in 1999. A comparison of West
Virginia and United States age-specific fertility rates is displayed in
the table below.
The 1999 U.S. fertility rate of 65.8 live births per 1,000 women aged
15-44 was 0.3% higher than the 1998 rate (65.6). West Virginia's fertility
rate increased from 53.7 in 1998 to 56.3 in 1999. A comparison of West
Virginia and United States age-specific fertility rates is displayed in
the table below.| Fertility
Rates* by Age Group West Virginia and United States, 1999 |
|||||
| 15-19 | 20-24 | Total (15-44) | |||
| WV | U.S.** | WV | U.S.** | WV | U.S.** |
| 47.3 | 49.6 | 58.2 | 68.7 | 56.3 | 65.8 |
* All fertility rates were calculated
using 1999 estimates, U.S. Department of Commerce, Bureau of the Census.
** National center for Health Statistics,
Monthly Vital Statistics Report, Vol. 48, No. 14, August 8, 2000.
The fertility rate among women aged 15-19 in West Virginia was 4.6% lower
than that among young women in the U.S. (47.3 vs. 49.6). The fertility
rate among women aged 20-44, however, was 15.3% lower in the state than
in the nation (58.2 vs. 68.7).
The number of births to teenage mothers decreased by 195 (6.1%), from 3,220 in 1998 to 3,025 in 1999. The percentage of total births decreased from 15.5% in 1998 to 14.6% in 1999. The significantly lower fertility rate among older women, however, resulted in teenage births continuing to constitute a higher proportion of total births than is found nationally (12.2% in 1999).
After rising steadily over the past decade, except between 1996 and 1997, the percentage of births occurring out of wedlock declined in 1999 although nearly one out of every three (31.7%) West Virginia resident births was to an unwed mother. The percentages of white and black births that occurred out of wedlock in West Virginia in 1999 were 30.1% and 77.9%, respectively, compared to 30.8% and 76.6% in 1998. In the United States in 1999, 26.7% of white births and 68.8% of births to black mothers occurred out of wedlock. The percentage of teenage births to unmarried teenage mothers in the state decreased from 71.0% in 1998 to 69.6% in 1999.
There were a total of 1,667 low birthweight babies (those weighing less than 2,500 grams or 5½ pounds) born to West Virginia residents in 1999, 8.0% of all births. Of the 1,571 low birthweight infants with known gestational age, 1,018 or 64.8% were preterm babies born before 37 weeks of gestation. (Of all 1999 resident births with a known gestational age, 13.5% were preterm babies.) Of the births with known birthweight, 12.2% of black babies and 7.9% of the white babies were low birthweight. Nationally, 7.6% of all infants weighed less than 2,500 grams at birth in 1999; 6.6% of white infants and 13.1% of black infants were of low birthweight.
Over eighty-five percent (85.1%) of West Virginia mothers who received known prenatal care began their care during the first trimester of pregnancy compared to 83.2% of mothers nationwide in 1999. Among those with known prenatal care, 85.7% of the white mothers began care during the first trimester; 70.8% of black mothers did so. No prenatal care was received by 0.5% of white mothers and by 1.3% of black mothers.
Over one-fourth (25.6%) of the 20,731 births in 1999 were to mothers who smoked during their pregnancies, while 0.6% of births were to women who used alcohol. The most recent national figures show that 12.9% of women giving birth reported smoking during pregnancy and 1.1% used alcohol (1998). Nearly one-fourth (24.9%) of 1999 state births were delivered by Cesarean section, compared to national rate of 22.0%. One or more complications of labor and/or delivery were reported for 32.6% of deliveries in the state in 1999.
Top of PageDeaths
Effective in 1999, the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS)
and World Health Organization (WHO) adopted the tenth revision to the
International Classification of Diseases - now known as ICD-10. This is
the first revision since 1979 and includes a more comprehensive classification
of causes of death. Previously, all causes of death were coded numerically.
Now all causes of death are coded alpha-numerically, allowing many more
possible causes (Table 42, pages 93-118). When comparing 1999 deaths to
earlier years, differences between ICD-9 coding and ICD-10 coding must
be taken into account. Appendix B contains a more detailed explanation
of ICD-10, as well as the new selected causes of death listing and comparability
ratios for examining similar categories of deaths using ICD-9 and ICD-10.
Due to the transition from ICD-9 to ICD-10, United States mortality figures
will not be released until the summer of 2001.
The number of West Virginia resident deaths increased from 20,764 in 1998
to 20,993 in 1999. The state's crude death rate also rose from 11.5 per
1,000 population to 11.6. The average age at death for West Virginians
was 73.2 (69.7 for men and 76.5 for women). One hundred and forty-seven
West Virginia residents who died in 1999 were age 100 or older. The oldest
man was 108 years old at the time of death, while the oldest woman was
110 years old.
Heart disease, cancer, and stroke, the three leading causes of death,
accounted for 62.1% of West Virginia resident deaths in 1999. Compared
to 1998, the number of state deaths due to heart disease increased 1.8%
while cancer deaths increased 0.1%. Deaths due to stroke increased (7.4%),
as did chronic obstructive pulmonary disease mortality (3.8%). Diabetes
mellitus deaths increased 1.4%, while the number of reported deaths due
to pneumonia and influenza decreased substantially (61.5%) from 1998 to
1999.* Mortality resulting from accidents increased 2.1%, from 814 in
1998 to 831 in 1999. Motor vehicle traffic accidents continued to be below
the 424 deaths in 1993, the year the West Virginia seatbelt law took effect,
decreasing by 11 (2.8%) from 386 in 1998 to 375 in 1999.
*The transition from ICD-9 to ICD-10 coding resulted in
markedly fewer deaths attributed to pneumonia and influenza.
Accidents remained the leading cause of death for ages one through 34 years. Even with the precipitous drop in motor vehicle accident deaths between 1993 and 1994, such fatalities remained the single leading cause of death for young adults aged 15 through 34, accounting for 32.2% of all deaths for this age group in 1999, compared with 30.2% in 1998. West Virginia's 1999 motor vehicle fatalities included six children under five years of age, compared to three in 1998.
Suicides increased by eight (224 to 232 or 3.6%) between 1998 and 1999. Male suicides increased 5.8%, from 189 in 1998 to 200 in 1999; the number of female suicides (32) decreased by three or 8.6% from 1998. Seventy-five percent (75.0%) of all suicide deaths were firearm related — 78.0% of male suicides and 56.3% of female suicides. The average age of death for a suicide victim in 1999 was 47.3 years. While suicide was the ninth leading cause of death overall, it was still the second leading cause of death for ages 15-34. The number of suicides among persons aged 19 and under dropped by two, from 17 in 1998 to 15 in 1999.
Homicides in West Virginia increased by seven, from 95 in 1998 to 102 in 1999. Seventy-two (72) of the homicide victims were male, 30 were female. The average age at death for a homicide victim in 1999 was 38.9 years. There was one homicide victim under the age of five in 1999, compared to three in 1998. Over sixty percent (61.8%) of 1999 homicide deaths were due to firearms.
Top of PageYears of Potential Life Lost (YPLL)
YPLL is a measure of premature or preventable mortality occurring before
the age of 65, calculated as the difference between age 65 and the age
at death. The sum of YPLL over all causes is the total YPLL from all persons
dying before the age of 65. For example, a person dying at the age of
45 contributes 20 years total to the total YPLL (65-45 = 20 YPLL). YPLL
is an important tool for emphasizing and evaluating causes of death among
persons less than 65 years of age.
The YPLL from all causes decreased slightly (1.7%), from 81,243 YPLL in 1998 to 79,854 in 1999. The three leading causes of YPLL in 1999 were malignant neoplasms (14,922 YPLL), diseases of the heart (13,013 YPLL), and motor vehicle accidents (10,525 YPLL). Combined, these three causes accounted for almost half (48.2%) of all years of potential life lost in 1999. In comparison to 1998, YPLL attributable to malignant neoplasms decreased from 19.0% of the total to 18.7%. YPLL due to diseases of the heart also decreased from 17.3% to 16.3% while the percentage of total YPLL due to motor vehicle crashes increased from 12.7% to 13.2%.
Top of PageInfant Deaths
Deaths of infants under one year of age decreased from 167 in 1998 to
157 in 1999. West Virginia's infant mortality rate decreased as well (6.2%),
from 8.1 per 1,000 live births in 1998 to 7.6 in 1999.
The table below shows the decline in the national and state infant mortality rates from 1950 through 1999. Data on U.S. infant mortality were not available for 1999 at the time of publication.
| 1950 - 1999 Infant Mortality West Virginia and United States (Number and Rate per 1000, Live Births |
||
| Year | West Virginia | United States |
| 1950 | 31.4 | 29.2 |
| 1955 | 27.1 | 26.4 |
| 1960 | 25.3 | 26.0 |
| 1965 | 27.1 | 24.5 |
| 1970 | 23.3 | 20.0 |
| 1975 | 18.3 | 16.1 |
| 1980 | 11.8 | 12.6 |
| 1985 | 10.7 | 10.6 |
| 1990 | 9.8 | 9.1 |
| 1991 | 8.1 | 8.9 |
| 1992 | 9.1 | 8.5 |
| 1993 | 8.6 | 8.3 |
| 1994 | 6.1 | 8.0 |
| 1995 | 7.6 | 7.5 |
| 1996 | 7.2 | 7.2 |
| 1997 | 9.5 | 7.2 |
| 1998 | 8.1 | 7.2 |
| 1999 | 7.6 | N/A |
The state's 1999 white infant mortality rate decreased 8.8%, from 8.0 in 1998 to 7.3, while the rate for black infants increased 26.4%, from 10.6 to 13.4 (see statistical variation in Methodology on page 9). West Virginia's 1999 race-specific infant mortality rates and comparable U.S. rates for 1998 are shown in the table below:
| 1999 West Virginia
and 1998 United States Infant Mortality by Race (Number and Rate per 1,000 Live Births) |
||||
| Race of Infant | West Virigina | United States | ||
| Number | Rate | Number | Rate | |
| All Races | 157 | 7.6 | 28,371 | 7.2 |
| White | 148 | 7.5 | 18,561 | 6.0 |
| Black | 9 | 12.1 | 8,726 | 14.3 |
| Other | 0 | 0.0 | 1,084 | 5.1 |
Approximately one in seven (13.4%) infant deaths in 1999 was due to SIDS (sudden infant death syndrome). Twenty-six percent (26.1%) were the result of congenital anomalies, while 48.4% were due to certain conditions originating in the perinatal period, including disorders relating to short gestation and unspecified low birthweight (12.1%).
Top of PageNeonatal/Postneonatal Deaths
The number of neonatal deaths increased by three, from 95 in 1998 to 98 in 1999; the neonatal death rate also increased marginally from 4.6 deaths among infants under 28 days per 1,000 live births in 1998 to 4.7 in 1999. Neonatal deaths comprised 62.4% of all West Virginia resident infant deaths in 1999, compared to 56.9% in 1998. The rate of postneonatal deaths decreased from 3.5 deaths per 1,000 neonatal survivors in 1998 to 2.8 in 1999.
Top of PageFetal Deaths
The 142 resident fetal deaths occurring after 20 or more weeks of gestation reported in 1999 were 17 more than the 125 fetal deaths in 1998. The fetal death ratio increased from 6.0 deaths per 1,000 live births in 1998 to 6.8 in 1999. The majority (85.9%) of fetal deaths were due to conditions originating in the perinatal period, including complications of placenta, cord, and membrane (33.1%), maternal conditions (4.2%), maternal complications (9.9%), short gestation and low birthweight (6.3%), and other ill-defined perinatal conditions (21.1%). Congenital anomalies accounted for 13.4% of all fetal deaths.
Top of PageMarriages
Due to a new law that became effective June 2, 1999* the number of marriages in West Virginia dramatically increased from 10,839 in 1998 to 13,705 in 1999. The marriage rate in 1999 was 7.6 per 1,000 population, compared to 6.0 in 1998. The state's 1999 marriage rate was 8.4% lower than the 1998 provisional U.S. rate of 8.3. (No 1999 U.S. data were available at time of publication.)
The median age for all marriages in 1999 was 25 for brides and 27 for grooms. For first marriages, the median age was 21 for brides and 23 for grooms. The mode (most frequently reported age) for all marriages was 22 for brides and 24 for grooms. For first marriages, the mode was 20 for brides and 22 for grooms.
*The new law removed the three-day waiting period for persons aged 18 and older as well as the requirement for a blood test for syphilis.
Top of PageDivorces and Annulments
The number of divorces remained the same in 1999 as in 1998 at 9,309. The 1999 rate of 5.2 per 1,000 population increased from 5.1 in 1998. The 1998 U.S. provisional rate was 4.2 per 1,000 population. (No 1999 U.S. data were available at time of publication.)
Of the 9,309 divorces in West Virginia in 1999, the median duration of marriage was six years. Over half (51.9%) of the divorces involved no children under 18 years of age in the family, while one child was involved in 25.3% of all divorces and two children were involved in 17.2%. Six divorces involved six or more children.
Top of Page Summary
The number of West Virginia resident births increased by two from 20,729
in 1998 to 20,731 in 1999. West Virginia resident deaths increased from
20,764 in 1998 to 20,993 in 1999. The number of infant deaths decreased
from 167 in 1998 to 157 in 1999. Fetal deaths of 20 or more weeks gestation
increased by 17, from 125 in 1998 to 142 in 1999. Marriages increased
for the second year in a row, from 10,839 in 1998 to 13,705 in 1999, while
divorces remained unchanged at 9,309.

| WV | DHHR| BPH | OEHP | HSC | PUBLICATIONS | TOP OF PAGE |